Online simple and compound interest calculator
This tool is used to calculate your interest in simple and compound mode.
It uses the United States decimal number format, for example: 1,234.56.
What is this online simple and compound interest calculator, and how does it work?
It is a free online simple and compound interest calculator that was made by the 'PU Tools' developer team. The number of uses is unlimited without any registration requirement.
It has two calculation modes: simple and compound, and it will calculate your interest based on your input values, including: 'Initial deposit', 'Interest rate', 'Number of periods', 'Regular deposit'.
With an optimized calculation algorithm, it will give you the exact results quickly, including: 'interest', 'total interest', 'ending balance' for each period.
'Total deposit', 'total interest' and 'total interest in percentage' will also be given after the calculation has finished.
Initial deposit: Your initial deposit amount, for example: 10,000.23. Format: Positive decimal number.
Interest rate: The interest rate for each period, for example: 5.5%. Format: Positive decimal number.
Number of periods: The number of your saving terms, for example: 5. Format: Positive integer number.
Regular deposit: Your extra investment for each period, for example: 1,000. Format: Positive decimal number. Enter 0 or leave it blank to ignore this input.
Your extra investment will be initialized and calculated at the beginning of the 2nd period (*).
Below is the test vector of compound mode with these parameters: Initial deposit = 10,000, Rate = 5%, Periods = 5, Regular deposit = 0.
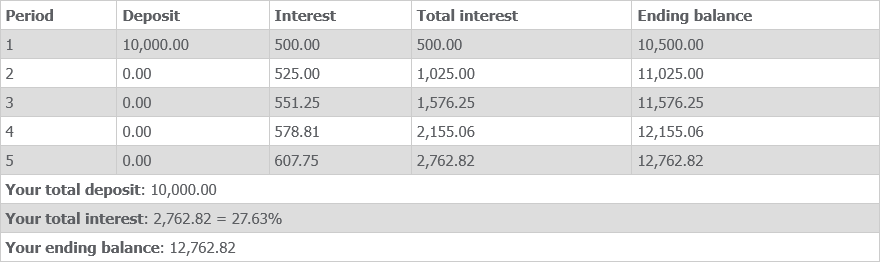
Explanation of the point (*):
If you have an initial deposit, for example: 10,000 and an extra deposit in Period[1], for example: 1,000.
So, why shouldn't the initial deposit just simply be 11,000?
That's why your regular deposit will be initialized and calculated at the beginning of the 2nd period.
In simple mode, your Period[2] investment amount = Initial deposit + Extra deposit.
In compound mode, your Period[2] investment amount = Initial deposit + Extra deposit + Period[1] interest.
Definition:
Initial deposit = P; Extra deposit = E; Number of periods = N; Interest = I; Total interest = EI; Ending balance = EB;
Simple mode calculation:
The 1st period: I[1] = P * R / 100; EB[1] = P + I[1].
The 2nd period: I[2] = (P + (E * 1)) * R / 100; EB[2] = P + (E * 1) + I[2].
The 3rd period: I[3] = (P + (E * 2)) * R / 100; EB[3] = P + (E * 2) + I[3].
Loop the calculation until the number of periods ends.
Total deposit = P + (E * (N - 1)).
EI = Sum of all interests, from I[1] to I[N].
EB = Total deposit + EI.
Compound mode calculation:
The 1st period: I[1] = P * R / 100; EB[1] = P + I[1].
The 2nd period: I[2] = (EB[1] + E) * R / 100; EB[2] = EB[1] + E + I[2].
The 3rd period: I[3] = (EB[2] + E) * R / 100; EB[3] = EB[2] + E + I[3].
Loop the calculation until the number of periods ends.
Total deposit = P + (E * (N - 1)).
EB = EB[N] after being calculated.
EI = EB - Total deposit.
What is interest?
Interest is a fundamental concept in finance and economics. It is the cost of borrowing money or the reward for saving or investing money.
Simple interest:
- If you deposit a principal amount in a bank or lend it to someone at a fixed interest rate. Simple interest is the interest you receive on that original principal amount over the entire period. This interest is not added to the principal to calculate interest for the following periods.
- Formula: Simple interest = Principal * Interest rate * Period.
Compound interest:
- Compound interest is interest that is calculated not only on the original principal but also on the interest accumulated from previous periods. This means that the interest earned is added to the old principal to create a new principal, which will continue to earn interest for the next period.
- It is a powerful tool for growing your wealth over time if you invest or save for the long term. "Compound interest is the eighth wonder of the world. He who understands it, earns it; he who doesn't, pays it." - Albert Einstein once said.
- Formula: EB = P * (1 + R)N.
--------------------------------------------------
Above is basic information about simple interest and compound interest. If you want to discover more, please visit: Compound interest on Wikipedia.
Check some bank savings interest in the United States: Bank of America, U.S. Bank, Wells Fargo Bank.
Related Tools
Our Popular Tools
Encryption Tools
Encoding Tools
Decoding Tools
Text Tools
Data Tools
Date and Time Tools
Finance Tools